

This recombines the alleles present on each chromosome, as seen in the image below. When the homologous chromosomes pair up, portions of the DNA on different chromosomes are able to swap. However, the homologous chromosomes also pair in prophase I. During prophase I, the chromosomes condense, as in mitosis.

Thus, when meiosis starts, there are two copies of each chromosome, attached as sister chromatids in the same chromosome. As in the case of interphase preceding mitosis, each chromosome is replicated during synthesis of interphase. The first division of meiosis, meiosis I starts after a cell goes through interphase. Meiosis consists of two separate cell divisions, separated by a phase known as interkinesis. There are two stages of prophase during meiosis. During prophase of mitosis, the molecular motors and necessary condensation of the DNA allows the sister chromatids to be separated. Each cell will still have homologous pairs of chromosomes that carry different alleles for each gene. In this way, the cells will be identical to the cell that existed before the DNA was copied. Like animals, the chromosomes condense and can be seen, and the nucleolus disappears during prophase.Īfter prophase of mitosis, the chromosomes with will attached to microtubules, arranged in the middle of the cell, and the sister chromatids of every chromosome will be separated into new cells. During preprophase, these mechanisms are set up.

Some plants also lack centrosomes, and organize their microtubules in different ways. In plants, a stage precedes prophase in which the nucleus is moved into the center of the cell, and the large water-filled vacuole is moved out of the way. It will be reassembled after the cells divide. Because the cell seizes to transcribe new RNA during cell division, this complex can be disassembled and distributed to each new cell. Ribosomes are the large protein and RNA complexes that create other proteins. The nucleolus is a dark spot in the nucleus that contains RNA and proteins responsible for creating ribosomes. Under a microscope, this stage can be seen as a darkening of different places in the nucleus.Īnother component of the nucleus, the nucleolus, disappears during prophase. At the onset of prophase, proteins associated with the DNA are activated, and the DNA winds around them and bundles in dense shapes. During interphase preceding mitosis, the chromosomes exist in a loose state. The first stage of mitosis is prophase, and it sets the stage for the later stages of mitosis. With a replicated genome and organelles, the cell can begin mitosis. This includes the centrosome, within which the centriole gets replicated. During interphase, the DNA is replicated, along with the organelles necessary to divide. Mitosis occurs after interphase in eukaryotes. Prophase begins cell division by separating the centers for these molecular motors, and condensing the chromosomes. These structures together are known as molecular motors and drive many cell processes. Organelles, chromosomes, and many other substances and structures are moved about the cell by microtubules and associated proteins.
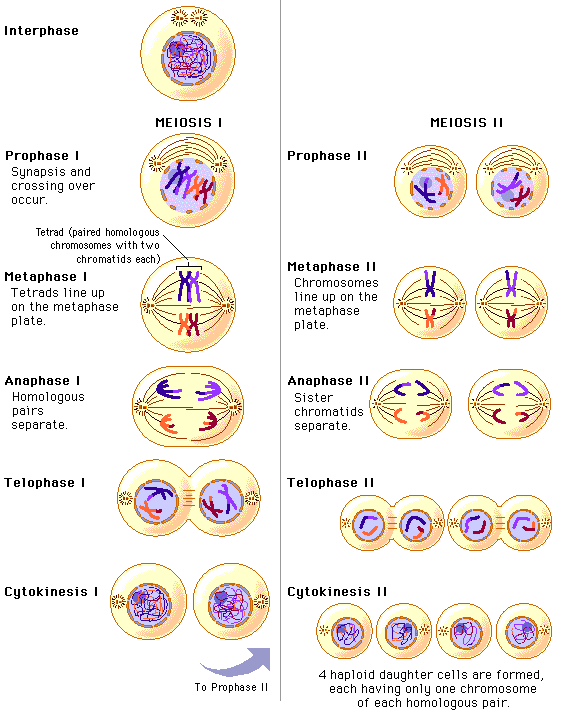
During prophase, they separate to provide microtubule centers in each new cell. This organelle controls the microtubules in the cell, and each centriole is one half of the organelle. Prophase, in both mitosis and meiosis, is recognized by the condensing of chromosomes and separation of the centrioles in the centrosome. Prophase is the starting stage of cell division in eukaryotes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
